6 Progressive GIS Tools Reshaping Spatial Analysis
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is experiencing an exciting revolution, driven by advances in artificial intelligence. Gone are the days when analysts spent countless hours manually collecting, analyzing, and interpreting spatial data. Today, we're witnessing the rise of innovative AI-powered tools that are transforming how we work with geospatial information. Whether it's using Extracto to automatically gather web data, harnessing CARTO's powerful cloud-based spatial analytics, or exploring new frontiers with AI navigation assistants like MapGPT, the field is evolving at an remarkable pace. In this article, we'll dive into five groundbreaking AI tools that are reshaping GIS, exploring how they're helping professionals work smarter, achieve better results, and make more informed decisions across industries.
extracto
Streamline web data collection for GIS with AI automation
Extracto.bot is a super handy AI-powered web scraping tool that works right inside Google Sheets, making life easier for GIS professionals. You don't need to mess with complicated setups - just add the fields you want as columns in your spreadsheet, go to the website and click extract. The tool does the rest which is pretty neat for keeping things organized in Google Drive.
The way it's designed really helps cut down on manual work and mental strain when you're gathering data. This is especially useful in GIS work where you might need to pull together lots of different kinds of information from various websites. For example you can quickly grab property details from real estate sites, collect business info for location studies or compare product specs from different vendors for managing assets. Since it works with Google Sheets, you can easily work with the data analyze it and share it with others.
They've got different pricing options that work for various needs and budgets. There's a free starter plan if you want to try it out and professional subscriptions if you need more features. This makes it pretty accessible whether you're working on a small project or something bigger that needs more horsepower.
Link: https://www.extracto.bot
CARTO
Cloud-native platform for modern spatial data analytics
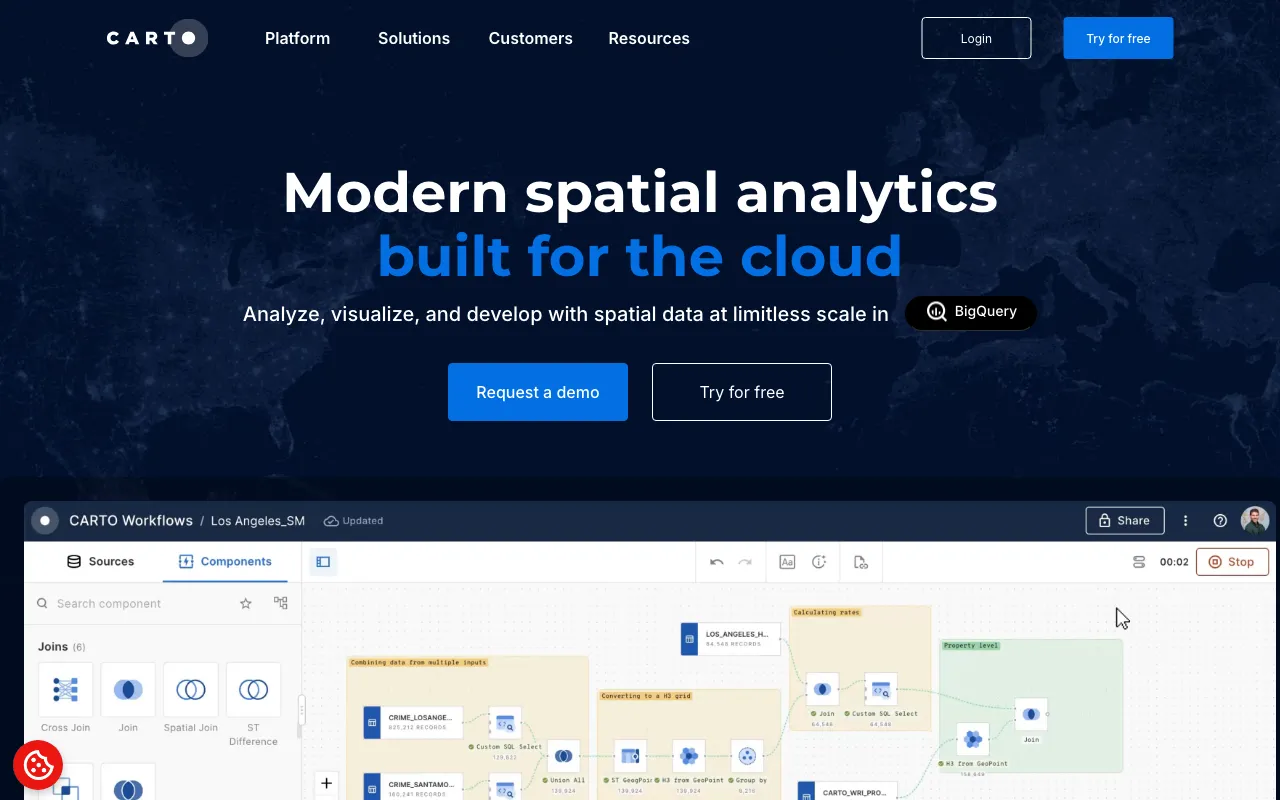
CARTO offers a cloud-native analytics platform that works smoothly with major cloud data warehouses like BigQuery, Snowflake, Redshift, Databricks and Azure. This setup lets GIS professionals use the power and scalability of these platforms to analyze, visualize and work with spatial data at massive scales. The platform includes a visual tool for designing workflows and automating analysis pipelines which means you don't need complex ETL processes or coding. With over 100 analysis tools ready to go and built-in AI features, CARTO helps users of all skill levels get better insights from their spatial data. The direct connection to existing cloud systems is really valuable for GIS teams looking to scale up without having to move data or rebuild infrastructure.
For GIS developers, CARTO provides a toolkit and APIs that work with any framework so they can build scalable map-based applications right in their cloud setup. The platform was built specifically to handle huge datasets directly from cloud warehouses and uses advanced visualization tools like deck.gl with WebGL and WebGPU for fast rendering. The AI features make things even easier by letting users interact with data using natural language and automate their workflow designs. This mix of cloud-native architecture, strong analytics capabilities and modern visualization tools makes CARTO a great choice for GIS professionals who want to update their workflows and get the most from their spatial data.
Link: https://www.carto.com/
MapGPT
AI-powered navigation assistant for dynamic location interactions
MapGPT is a location-aware AI assistant from Mapbox that's changing how we handle in-vehicle navigation and companion apps. It works with live Mapbox data and connects deeply with navigation software, letting users have natural conversations about their surroundings. People can ask about directions get traffic updates in real-time, find charging stations for their EVs and discover interesting places nearby. What makes it really useful is how it understands partial information and different languages, making it easy for anyone to use.
The system lets you control things hands-free, which is great for searching destinations and managing your navigation while driving. It connects with your vehicle's systems so you can check things like battery levels and control the temperature. You can even make restaurant reservations through partner integrations, which is pretty convenient.
For GIS professionals and developers, MapGPT is a big step forward. It uses constantly updated location data from Mapbox, enabling detailed conversations about changing elements like directions landmarks and road conditions. This real-time capability is essential for GIS applications that need current accurate data. GIS developers can customize the assistant by adding their own data sources like specific vehicle information or points of interest that matter for their projects. An important feature for field work is the offline mode which uses an onboard Tiny LLM to keep basic functions working without internet. Plus, it works with the Mapbox Dash SDK giving developers flexibility to add AI conversations to their GIS applications.
Link: https://www.mapbox.com/mapgpt
supervise
All-in-one platform for AI-powered GIS data labeling.

Supervisely helps GIS teams work with computer vision by providing tools for handling different types of spatial data. The platform works with regular images videos, LiDAR point clouds and DICOM volumes which makes it really useful for geospatial analysis. GIS professionals use it to build training datasets for finding objects, extracting features and spotting changes over time.
One of the best things about Supervisely is its smart labeling tools that use neural networks to speed up the annotation process. Teams can work together smoothly using shared workspaces and data management features while keeping everything organized with role-based access controls. Quality checks help make sure the data stays accurate which is super important for GIS work.
The platform goes beyond just labeling data. It creates an environment where you can train and use neural networks right in your browser. "Unlike other products, we create the true platform that integrates countless open-source tools and custom built solutions within a single ecosystem using Supervisely Apps" according to their website. These web apps let users do everything from training advanced models to creating synthetic data for better results.
What makes Supervisely especially good for GIS is how it handles the whole AI workflow from start to finish. You can customize labeling interfaces and dashboards to match exactly what your GIS project needs, and the platform brings together all the tools you need in one place. This makes it easier for GIS teams to use AI without jumping between different software.
Link: https://www.supervise.ly/
Picterra
AI-powered platform for custom geospatial object detection
Picterra is a cloud-based GeoAI platform that makes geospatial analysis easier by letting users create their own AI models for finding objects, tracking changes and spotting patterns in images. The platform works with many types of imagery including satellite, aerial and drone data across different spectral bands like RGB, multispectral, SAR, NIR, NDVI, thermal and height maps. What's really impressive is how quickly you can develop models - often in just a few hours which helps GIS professionals get insights fast from their data.
The platform connects smoothly with common tools like Esri ArcGIS Pro and Safe FME and includes interactive dashboards for sharing results efficiently. It's especially useful for industries such as mining, agriculture, forestry and infrastructure where it helps with tasks like compliance monitoring (including EUDR), managing resources and assessing risks.
What makes Picterra stand out is how it speeds up geospatial work dramatically turning what used to take months into hours of work. This helps GIS teams tackle complex challenges more efficiently while making it easier to work together. The platform is built to grow with your needs and includes API access particularly through their Picterra Tracer product which is great for monitoring and verifying plots. By combining custom AI models, support for different data types and integration with existing GIS workflows Picterra has become a powerful tool for anyone wanting to use AI in their geospatial analysis work.